Insert function
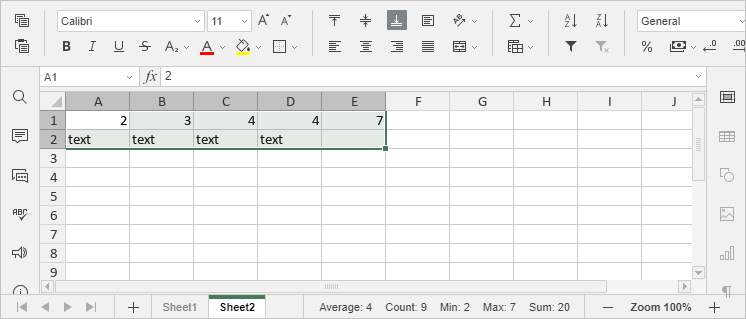
The ability to perform basic calculations is the principal reason for using a spreadsheet. Some of them are performed automatically when you select a range of cells in your spreadsheet:
- Average is used to analyze the selected range of cells and find the average value.
- Count is used to count the number of the selected cells containing values ignoring empty cells.
- Min is used to analyze the range of data and find the smallest number.
- Max is used to analyze the range of data and find the largest number.
- Sum is used to add all the numbers in the selected range ignoring empty cells or those contaning text.
The results of these calculations are displayed in the right lower corner at the status bar.
To perform any other calculations you can insert a needed formula manually using the common mathematical operators or insert a predefined formula - Function.
The possibilities to work with Functions are accessible from both Home and Formula tab. At the Home tab, you can use the Insert function button to add one of commonly used functions (SUM, MIN, MAX, COUNT) or open the Insert Function window that contains all available functions classified by category.

At the Formula tab you can use the following buttons:
- Function - to open the Insert Function window that contains all available functions classified by category.
- Autosum - to quickly access the SUM, MIN, MAX, COUNT functions. When you select a functions from this group, it automatically performs calculations for all cells in the column above the selected cell so that you don't need to enter arguments.
- Recently used - to quickly access 10 recently used functions.
- Financial, Logical, Text and data, Date and time, Lookup and references, Math and trigonometry - to quickly access functions that belongs to the corresponding categories.
- More functions - to access the functions from the following groups: Database, Engineering, Information and Statistical.
- Calculation - to force the program to recalculate functions.
To insert a function,
- select a cell you wish to insert a function into,
- proceed in one of the following ways:
- switch to the Formula tab and use the buttons available at the top toolbar to access a function from a specific group, or use the Additional option from the menu to open the Insert Function window;
- switch to the Home tab, click the Insert function icon, select one of the commonly used functions (SUM, MIN, MAX, COUNT) or click the Additional option,
- right-click within a selected cell and select the Insert Function option from the contextual menu,
- click the icon before the formula bar,
- in the Insert Function window that opens, select the necessary function group, then choose the function you need from the list and click OK.
- enter the function arguments either manually or dragging to select a range of cells to be included as an argument. If the function requires several arguments, they must be separated by commas.
Note: generally, numeric values, logical values (TRUE, FALSE), text values (must be quoted), cell references, cell range references, names assigned to ranges and other functions can be used as function arguments.
- Press the Enter key.
To enter a function manually using the keyboard,
- select a cell,
- enter the equal sign (=)
Each formula must begin with the equal sign (=).
- enter the function name
Once you type the initial letters, the Formula Autocomplete list will be displayed. As you type, the items (formulas and names) that match the entered characters are displayed in it. If you hover the mouse pointer over a formula, a tooltip with the formula description will be displayed. You can select the necessary formula from the list and insert it by clicking it or pressing the Tab key.
- enter the function arguments
Arguments must be enclosed into parentheses. The opening parenthesis '(' is added automatically if you select a function from the list. When you enter arguments, a tooltip that contains the formula syntax is also displayed.
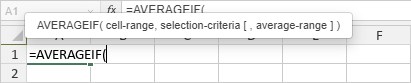
- when all the agruments are specified, enter the closing parenthesis ')' and press Enter.
If you enter new data or change values used as arguments, recalculation of functions is performed automatically by default. You can force the program to recalculate functions by using the Calculation button at the Formula tab. Click the Calculation button itself to recalculate the entire workbook, or click the arrow below the button and choose the necessary option from the menu: Calculate workbook or Calculate current sheet.
You can also use the following key combinations: F9 to recalculate the workbook, Shift +F9 to recalculate the current worksheet.
Here is the list of the available functions grouped by categories: